Networking is the exchange of information and ideas among people with a common profession or special interest, usually in an informal social setting. I recently felt like I had trouble remembering some of the stuff related to networking. Thus, I decided to take a small refresher and write stuff down so that they would stick with me better! What better way than to blog about it? 😏
IP Addressing (Layer 3)
IPV4
- Decimal notation
- 32 bits
IPV6
- Hexadecimal notation
- 128 bits
Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Network address translation is a method of remapping one IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device.
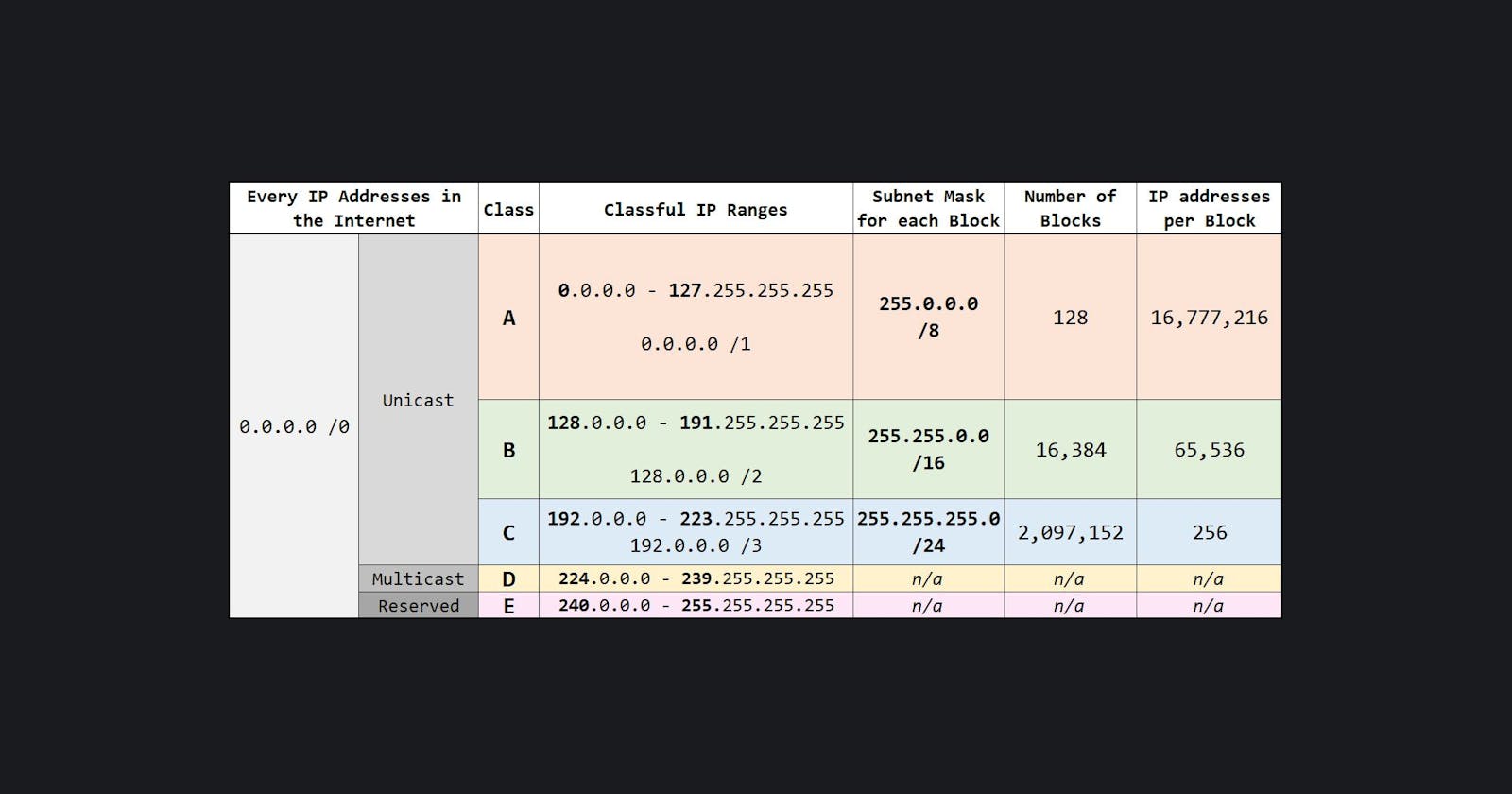
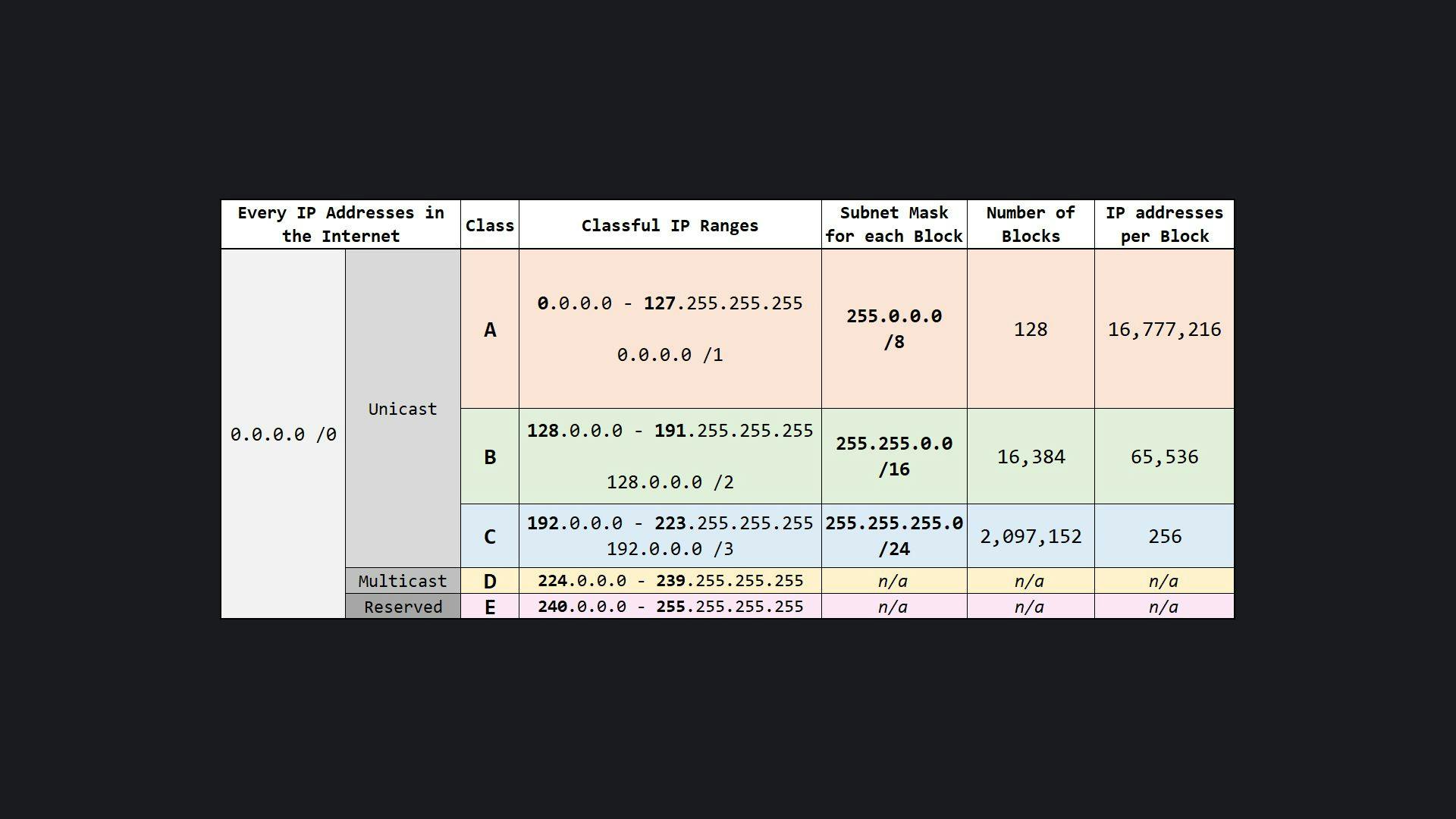
Classful Network
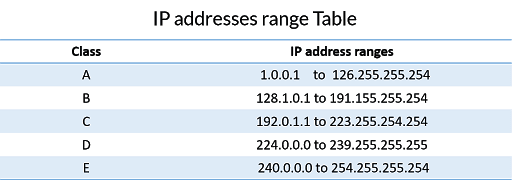
A classful network is a network addressing architecture used in the Internet from 1981 until the introduction of Classless Inter-Domain Routing in 1993. The method divides the IP address space for Internet Protocol version 4 into five address classes based on the leading four address bits.
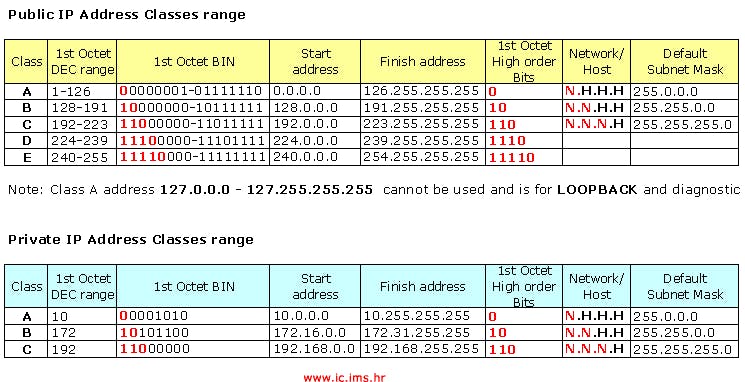
Private / Public IP Address classes
MAC Addresses (Layer 2)
A media access control address is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller for use as a network address in communications within a network segment. This use is common in most IEEE 802 networking technologies, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.
- Related to switching
- 48 bits
- Contains 6 pairs of twos [00:0c:29:78:a2:a2]
- First 3 pairs/half = Identifier [Able to identify the vendor of the NIC]
TCP, UDP and the Three-Way Handshake
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a standard that defines how to establish and maintain a network conversation through which application programs can exchange data. [Connection oriented protocol]
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is an alternative communications protocol to Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) used primarily for establishing low-latency and loss-tolerating connections between applications on the internet. [Connection-less protocol]
A three-way handshake is a method used in a TCP/IP network to create a connection between a local host/client and server
TCP
- Connection-Oriented Protocol
- High Reliability
- HTTP
- HTTP
- FTP
- SSH
How does the TCP Three-way handshake work?
To Initiate a connection:
SYN → SYN, ACK → ACK
To gracefully terminate a connection:
FIN → FIN, ACK → ACK
UDP
- Connection-less Protocol
- Less Reliable
- Streaming
- DNS
- VOIP
Common Ports and Protocols
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- FTP | 21
- SSH | 22
- Telnet | 23
- SMTP | 25
- DNS | 53
- HTTP | 80
- HTTPS | 443
- POP3 | 110
- SMB | 139 + 445
- IMAP | 143
- UDP (User Diagram Protocol)
- DNS | 53
- DHCP | 67 . 68
- TFTP | 69
- SNMP | 161
The OSI Model
The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology.
1 | Physical → data cables, Cat6
2 | Data link → Switching, MAC Addresses
3 | Network → IP Addresses, Routing
4 | Transport → TCP, UDP
5 | Session → Session Management
5 | Presentation → WMV, JPEG, MOV
6 | Application → HTTP, SMTP